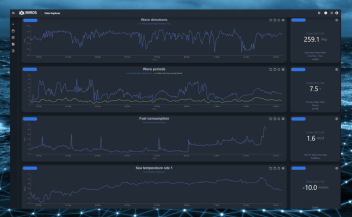
Air Gap: Why Measure It at All?
Real-time measurements of air gap can dispel uncertainty when vessels transit beneath bridges, aiding in the avoidance of collisions and ensuring that vessel transit continues according to schedule.
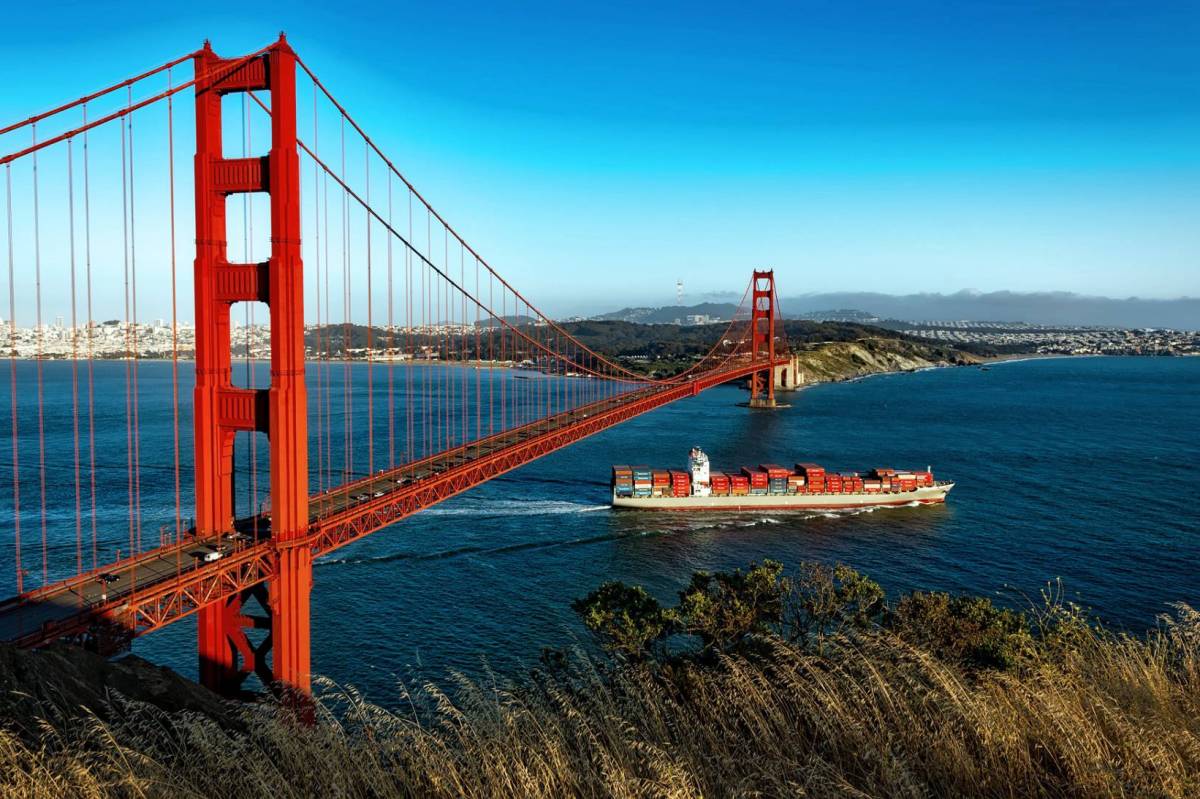



Even during a pandemic, thousands of container ships transit between ports and harbours across the globe, with ship operators relying on information about oceanic conditions to plan routes efficiently. The more accurate and reliable the data is, the greater operators’ abilities to reduce transit delays, maximise cargo loads, and ensure safe navigation without collisions or oil spills. As global demand for maritime transportation continues to grow, large vessels such as cargo carriers, oil tankers and cruise liners are increasing in size, bringing additional challenges for navigational safety.
Greater vessel size translates to increased vessel height, raising the risk of collisions when navigating under bridges, and since one additional foot of draft may account for between $36,000 and $288,000 more profit per transit, navigation systems that help maximise cargo loads whilst reducing uncertainties in under-keel clearances are becoming ever-more essential. Such systems rely on an availability of real-time insights into local currents, water levels and wind to increase the amount of cargo moved through a port or harbour by enabling mariners to safely utilise every inch of dredged channel depth available to them.
Why Do We Need to Measure Air Gap?
The depth of water and the height of bridges leading to ports or harbours are often seen as limiting factors for port prosperity. Many vessels will avoid specific harbours altogether if bridge clearance (air gap) is frequently a challenge. Air gap, after all, is constantly in flux and although tides are a major source of the variation, additional sources can include rivers, wind, waves, bridge altitude variations caused by varying traffic loads, and temperature-related structural expansion and contraction. Thus, many variables interact to determine air gap beneath a bridge at any given time.
The ability to offer accurate, real-time air gap measurements can work to dispel the challenges and uncertainties associated with navigating beneath bridges, enabling worry-free access to previously limited ports and harbours, and the economic gains increased commerce brings.
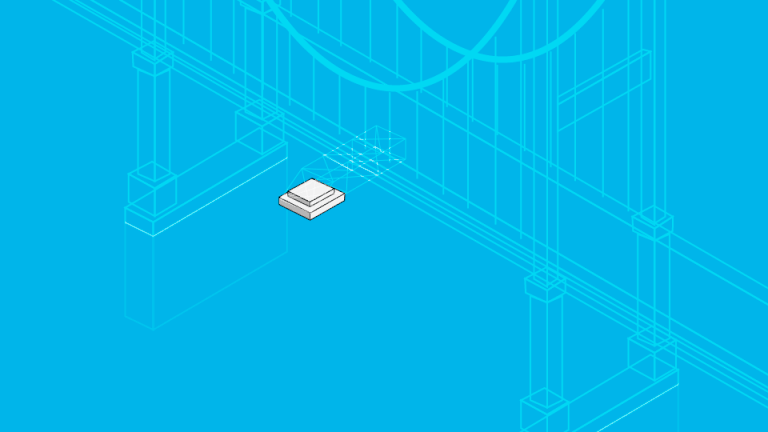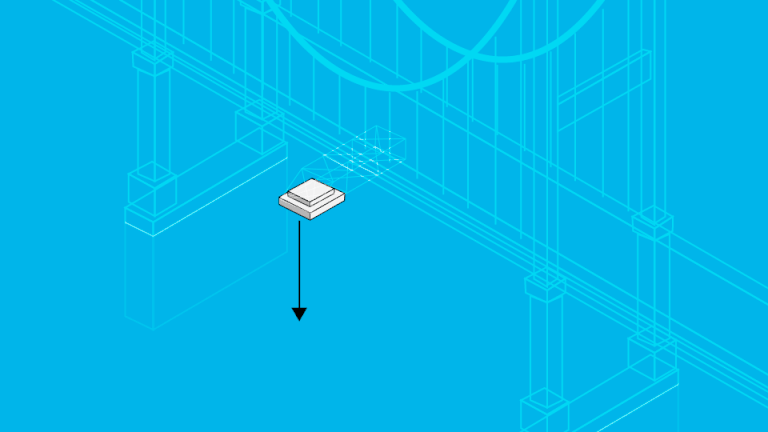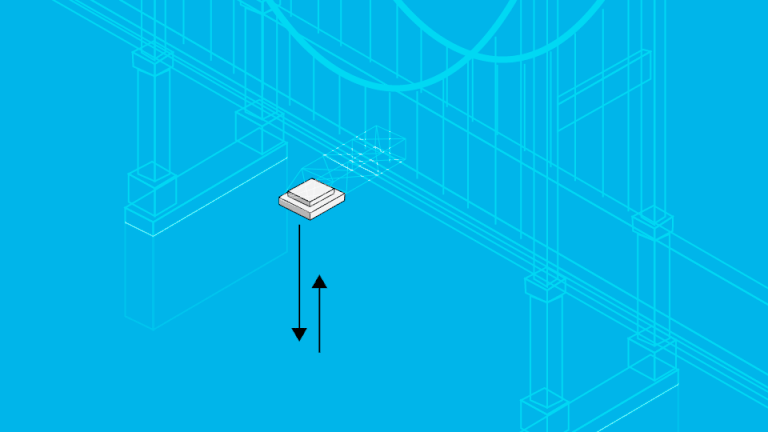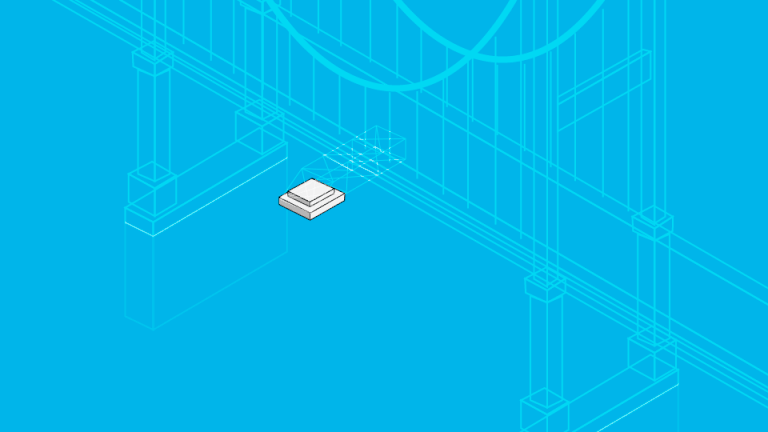
How Does the Miros Air Gap Solution Work?
The Miros RangeFinder measures the vertical distance between the bottom of a bridge and the surface of the water flowing underneath it, doing so with market-leading range (up to 95m) and accuracy (±5mm). Additionally, the RangeFinder’s radar-based measurements are not impacted by fog, rain or water spray, allowing for continuous situational awareness regardless of weather conditions. The RangeFinder measures in real time, accounting for changes in water level and bridge height as they develop. This means that captains can access true, moment-to-moment measurements of the distance beneath bridges, avoiding all uncertainties and ensuring safe navigation.
Find out more about the Miros RangeFinder by accessing our dedicated on-demand webinar here.


